INPUT SENSORS AND ACTUATORS ON-VEHICLE
TOYOTA COROLLA 2002Y, ENGINE 1ZZ-FE
Everything in the vehicle starts from the battery. Our engine battery is fully charged and alternator is working properly. Voltage supplied to the fuel injectors is 14.3 V.
Fuel injector is electronic device which is built on the basis of solenoid. This solenoid is supplied with battery voltage when engine is not running but the ignition switch is "on" and alternator voltage when engine is running. It is triggered by the power transistor on the earth side. When the circuit is completed by grounding injector is opened. When circuit is disconnected from ground injector is closed. Less level of voltage can bring to the situation when injector is opened less than it should be. As a result, any difficulties with engine start are possible. In practice engine can start but surging occurs at idle.
If there is excessive voltage drop (more than 0.05 V) between battery and injector, it’s a sign of poor connection either in the circuit or inside of the main relay. This is related with relays contacts condition. As an effect, the injectors’ productivity can be less than the specification figures.
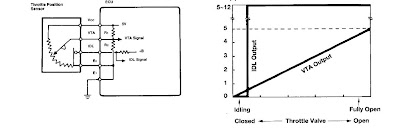
Circuit Diagram for the TPS
Our engine TPS sensor has three wires: brown- ground, yellow- 5 V reference, green-VTA signal.
As we can see on the photos voltage reading is very close to the Toyota spec. TPS works evenly, there is no signs of wear.
The reference voltage to the TPS is actually voltage supply for the voltage divider. The TPS is a variable resistor in its construction. And this resistor is part of the voltage divider. The proportion of voltage dissipating across the potentiometer gives reading to the ECU.
Incorrect reference voltage could give wrong voltage reading to the ECU. Taking in account that TPS signal provides the information of driver’s intention, wrong signal will affect the ECU commands to the fuel injection and ignition systems. This signal could not fit the current situation. As a result, it will be wrong proportion of air/fuel mixture, less performance, higher consumption.
According to the wiring diagram TPS ground wire is connected to the ECU. Thus, measuring the voltage drop (0.01 in our test) we check what the connection to earth is normal. It helps to eliminate any losses of supply voltage and incorrect signal readings. The cause of this can be loose connectors, corrosion on the contacts or bolted surfaces.
TPS WITH IDLE SWITCH FOR 4A-FE ENGINE
Another example for the TPS sensor is the one with four wires. Schematic diagram for this sensor as follows:
TPS WITH IDLE SWITCH FOR 4A-FE ENGINE
Another example for the TPS sensor is the one with four wires. Schematic diagram for this sensor as follows:
Once the batterfly is opened more than 1.5 deegres the idle signal is equal to the Vcc. Before this point the switch is earthed and so that the Idle signal is 0V. The video clip illustrates how the experiment was held:
THROTTLE POSITION SWITCH FOR NISSAN 6-CYLINDERS IN-LINE ENGINE.
All the wires on this switch are black. To conclude what type is this switch and how is it wired we checked voltage on the each pin of connector. This procedure reveiled that this switch diagram must be drawn like this:
Battery charge was pretty low, 10.8 V. But it was not the last loss. Test of voltage changes depending on the throttle angle and test of resistance depending on the throttle angle proved that Idle switch is faulty while PSW switch was working.
This device should have been working as follows:THROTTLE POSITION SWITCH FOR NISSAN 6-CYLINDERS IN-LINE ENGINE.
All the wires on this switch are black. To conclude what type is this switch and how is it wired we checked voltage on the each pin of connector. This procedure reveiled that this switch diagram must be drawn like this:
Battery charge was pretty low, 10.8 V. But it was not the last loss. Test of voltage changes depending on the throttle angle and test of resistance depending on the throttle angle proved that Idle switch is faulty while PSW switch was working.
when throttle is at Idle and opened less than 1.5 degrees the ECU gets reading of battery voltage. Further opening of the throttle gives the ECU 0V reading. Once the throttle reaches 70 degrees the PSW signal gives reading of battery voltage. Between this two readings the ECU understand that throttle in the midle. Not such a precise signal compared to the linear type TPS.
Circuit Diagram for the ECT
Reading for the ECT sensor in our experiment is 3.579 V when the engine is cold. According to the spec this reading is right for this temperature. After two minutes run the engine got wormer and the reading was 2 V.
That proves that ECT sensor is thermistor with NTC ( negative temperature coefficient). The wormer the engine, the lower resistance. This thermisor is part of the voltage divider. Signal from here goes directly to the ECU. the ECU processes is as follows:
1. cold engine, high voltage, the fuel mixture is richer.
2. worm engine, low voltage, the fuel mixture is leaner.
Incorrect voltage reading affects the ECU commands for actuators. Excessive enrichment leads to the extra consumption of fuel during cruising mode. And when the engine is cold, lean mixture will affect start. In some cases will be hard to start engine.
Measuring voltage drop on the ground side of our circuit we concluded that there is no evidence of poor grounding. The meter reading is 0.03 mV what is perfect. Otherwise wrong voltage signal for the ECU could affect it work. Incorrect air fuel mixture will be a result of this. And once again, ground for all sensors is common. So, if one sensor ground is playing, it is possible to get problem with other readings.
Circuit Diagram for the Crank Position Sensor
The attempts to measure AC voltage gave us 0.609 V at idle engine speed. and 1.059 V at 2500 rpm. For the DC scale figures are 0.34 V at idle and 0.64 V at 2500 rpm. Measuring frequency we have 340 Hz and 1.17 KHz accordingly. Frequency scale gives more information about "on" and "off" pulses of Crank sensor.
AC scale gives root-mean-square measurement only, what is not precise. The effectiveness of DC scale in this case is doubtful as well, because the result on the display depends on the circuitry of the meter. Hz scale at least shows particular changes from "off" to "on" state. However, none of these methods of signal control does not allow to diagnose this sensor state properly. Oscilloscope is the best tool for this.
The ECU use Crank sensor signal for the RPM reading . Frequency of the signal is proportional to the engine speed. This information is used for the ignition timing. To much advanced or retarded ignition timing affects engine performance and so that it is related with fuel consumption end emission.
MAP SENSOR
MAP sensor of 1ZZ-FE engine is mounted on the bracket which is attached to the bulkhead. Its function is to produce the signal of the engine load for the ECU. At the ignition key on position the reading we got is 0 V. At idle meter shows 0.02 V, and with quick but short acceleration we’ve got 0.037 V. This tells us that the lower negative pressure inside the intake manifold the higher voltage reading.
Wiring Diagram for MAP sensor:
If we look at the tipical graph of voltage variation with relation to the "vacuum" variation for Toyota engine we can conclude that our MAP sensor is within the spec.
MAP sensor signal is signal about the engine load. With incorrect signal from the MAP sensor the ECU produces a wrong signal for the ignition system first of all. Possible losses in performance and ineffective fuel consumption can be expected in such kind of situation.
MAF SENSOR TESTING ON THE LAND ROVER ENGINE
The connector layout is:
#1-temperature sensor
#2-battery voltage
#3-ground
#4-reference voltage (4.85V)
#5-signal to the ECU
AS it is seen from the photos with the engine not running reading for frequency is 0 Hz.
With the short acceleration of the engine frequency rises.It is obvious that the signal to the ECU changes with frequency in direct proportion, the higher air flow the higher the signal frequency.
IAT ( Intake Air Temperature)
IAT is actually thermistor with NTC (negative temperature coefficient). This property of IAT gives high voltage reading when it's cold. In our case it was 3.08 V with ignition on but not running engine.
Compared to the ECT sensor IAT is colder. As temperature of this device rises the resistance goes down. This happens when air passes through induction pipe and cools this sensor. This air flow is a cause of voltage changes. So that, quantity of air, coming into the engine, can be calculated by the ECU in accordance to voltage going down.
Wrong reading brings wrong command signal for the amount of fuel being injected in a certain period of time. As a result, air fuel ratio is going to be affected.
IAT is wired to the circuit as follows :
Camshaft Position Sensor(CMP)
CAM sensor for 1ZZ-FE is inductive type sensor which produces voltage indused in the pickup coil.. This sensor is actually similar to the AC generator in its function. Wave shape is close to the sinusoid type. However, shape of the relactor's teeth affect the form of the signal. Once the relactor rotates faster it will be increase in amplitude ind in frequency of the signal.The schematic diagram below represents the idea of how it is built:
The readings from multimeter are :
DC : 131mV
AC:1.5 V
HZ: 30 Hz
DC and AC don’t give much information. The momentum, at which signals changes from high to low, cannot be registered properly. The duty cycle and frequency allow controlling the signal "on" and "off" time. However, oscilloscope is still the best measuring and diagnostic tool for this purpose.




























Some good work however you forgot to update your Land rover MAF tests from frequency to voltage
ReplyDelete